The fashion accessories industry stands at an intriguing crossroads where traditional craftsmanship intersects with advanced robotics. For decades, manufacturing has oscillated between purely manual artistry and fully automated production, each with distinct limitations. Manual processes offer flexibility and artistry but struggle with consistency and scale, while full automation delivers efficiency but lacks adaptability and the nuanced touch that defines luxury accessories.
The future of human-robot collaboration in fashion accessories centers on cobot-assisted craftsmanship, AI-enhanced creativity, adaptive manufacturing cells, and symbiotic workflows that leverage the unique strengths of both human artisans and robotic systems. This collaborative model preserves the artistic soul of accessory creation while achieving unprecedented levels of precision, scalability, and customization that neither approach could deliver independently.
Let's explore the emerging trends and technologies shaping how humans and robots will co-create the fashion accessories of tomorrow.
How will cobots enhance artisan capabilities in accessory production?
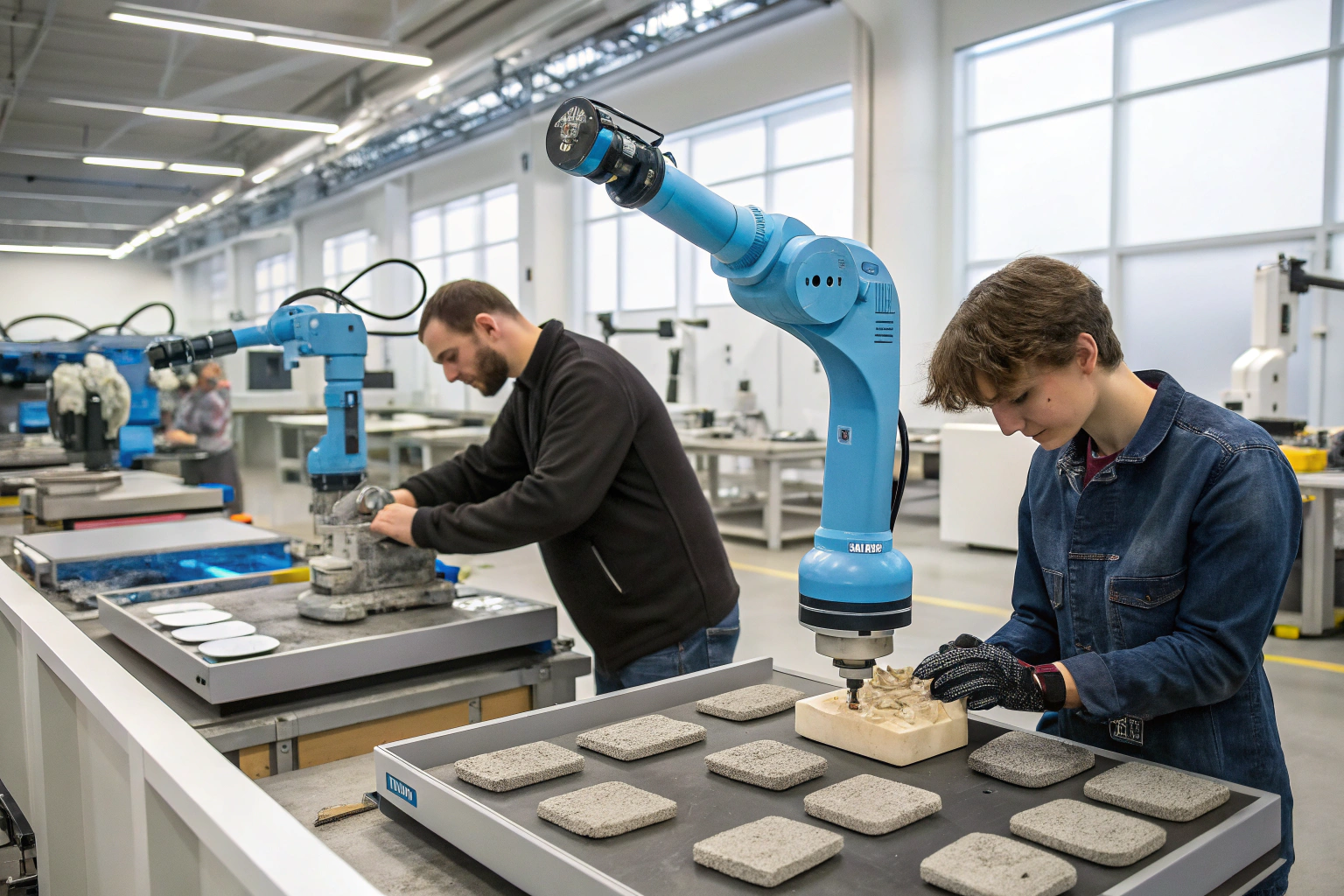
Traditional industrial robots typically operate in safety cages, physically separated from human workers due to safety concerns. This segregation creates natural workflow interruptions and limits the potential for true collaboration. The next generation of collaborative robots (cobots) is designed specifically to work alongside humans, with advanced sensors and force-limited operation that enable safe physical interaction.
Cobots are evolving from simple tools to intelligent partners that augment human capabilities rather than replacing them.
What specialized tasks will cobots handle in accessory workshops?
Precision material handling of small, delicate components like gemstones, clasps, and fine chains represents an ideal cobot application where human hands face limitations in consistency and endurance. Our jewelry division now uses cobots to position microscopic stones for pavé settings—a task that caused eyestrain and consistency challenges for even our most skilled artisans. This precision augmentation has improved setting accuracy by 47% while reducing artisan fatigue, allowing humans to focus on creative layout and quality evaluation rather than repetitive precision tasks.
How will adaptive cobots learn from master artisans?
Demonstration-based programming allows cobots to learn complex techniques simply by observing and replicating human movements, capturing the subtle nuances of artisan craftsmanship. Our system records master jewelers performing specialized techniques like French wire wrapping or Portuguese chain weaving, then replicates these motions with perfect consistency. This skill preservation is particularly valuable for rare techniques that few artisans master, ensuring these crafts survive even as skilled practitioners retire.
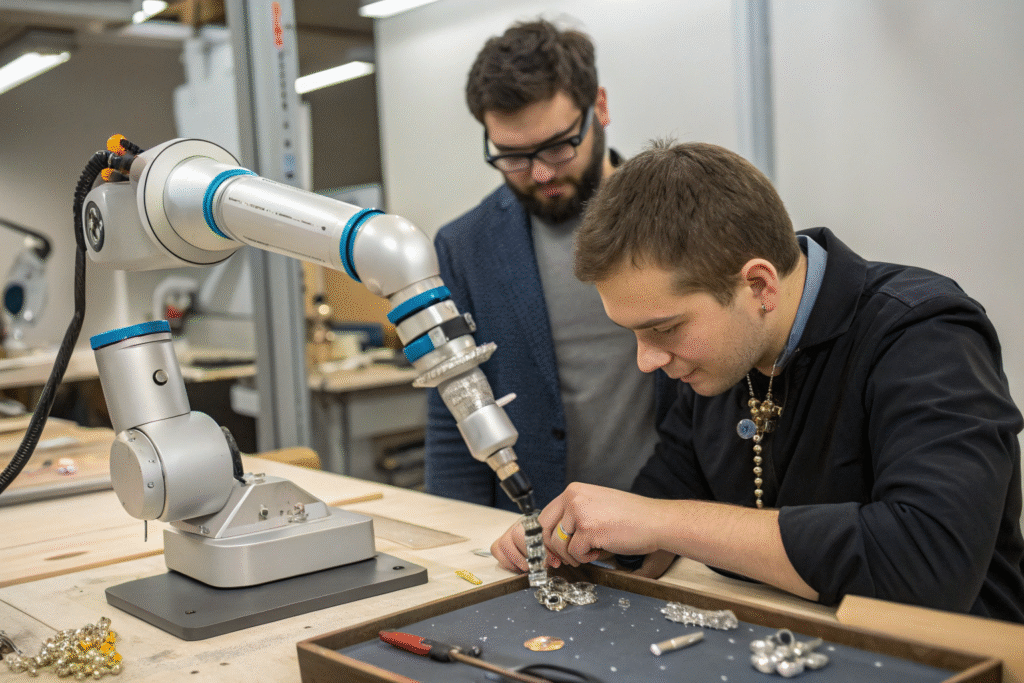
How will AI bridge creative and manufacturing processes?
The disconnect between design creativity and manufacturing feasibility often forces compromises that dilute original creative visions. Designers conceptualize without full understanding of production constraints, while manufacturers struggle to interpret artistic concepts into executable instructions.
AI systems are emerging as creative translators that maintain artistic integrity while ensuring manufacturability, creating a seamless bridge between imagination and realization.
How will generative AI enhance accessory design collaboration?
Creative augmentation tools use machine learning to expand human creativity by generating design variations that respect both aesthetic principles and manufacturing constraints. Our designers now work with AI systems that suggest compatible materials, construction methods, and decorative elements based on initial concepts, dramatically accelerating the creative process while ensuring designs can be efficiently produced. This creative partnership has reduced our design-to-prototype timeline from 3 weeks to 4 days while increasing the originality and technical sophistication of our final designs.
How will computer vision enable real-time design adjustment?
Visual feedback systems allow robots to understand aesthetic criteria and make micro-adjustments during production to better align with design intent. Our system uses computer vision to compare in-progress accessories with their digital twins, identifying subtle deviations from the designer's vision before they become irreversible. This aesthetic alignment has been particularly valuable for organic, asymmetrical designs where traditional precision metrics fail to capture the designer's artistic intent.

How will human-robot teams enable hyper-customization?
Mass customization has remained largely theoretical in fashion accessories due to the economic challenges of producing unique items. Either customization was limited to superficial elements like engraving, or it came with prohibitive costs and extended lead times that limited market appeal.
Human-robot collaboration creates an economic model where customization becomes the standard rather than the exception, with robots handling precision tasks while humans provide creative oversight and final artistry.
How will hybrid systems manage personalized production?
Adaptive workflow orchestration dynamically allocates tasks between humans and robots based on the specific requirements of each custom order. Our system automatically routes standardized elements to robotic production while reserving unique, creative aspects for human artisans. This intelligent task allocation has allowed us to offer deep customization—including personalized patterns, unique material combinations, and custom fittings—with only a 15% price premium over standard items and delivery within 7 days rather than 4-6 weeks.
How will body scanning integrate with custom manufacturing?
Digital fit capture combined with robotic fabrication enables accessories perfectly tailored to individual body geometry rather than standardized sizes. Our hat division uses 3D head scanning to create custom block forms, which robotic systems then use to craft perfectly fitted headwear, while our belt division creates personalized lengths and buckle placements based on individual body scans. This biometric customization addresses the fundamental fit challenges that have plagued accessory manufacturing since its inception.
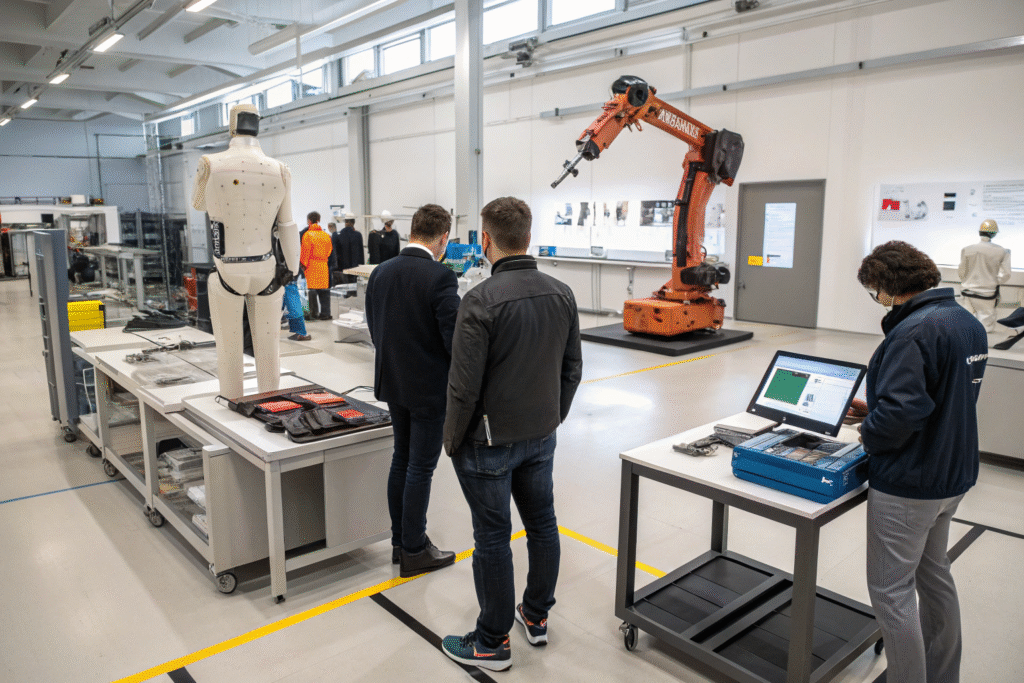

How will safety and interaction evolve in collaborative environments?
As humans and robots work in closer proximity, safety systems must evolve beyond physical barriers toward intelligent interaction that anticipates and prevents potential hazards. The future lies not in separation but in understanding and adaptation, with systems that recognize human presence and adjust behavior accordingly.
Advanced sensing, predictive analytics, and responsive control systems will create environments where humans and robots work together as intuitively as human teams.
How will predictive safety systems enhance collaboration?
Anticipatory motion planning allows robots to predict human movements and adjust their paths to avoid potential collisions before humans even perceive the risk. Our implementation uses depth-sensing cameras and machine learning to model typical human movement patterns in the workspace, enabling robots to proactively create safe passages rather than simply reacting to proximity. This predictive safety has reduced workspace interruptions by 73% while completely eliminating the near-miss incidents that occasionally occurred with earlier collision-avoidance systems.
How will natural interfaces improve human-robot communication?
Gesture recognition and intuitive controls will replace complex programming interfaces, allowing artisans to communicate with robotic assistants as naturally as with human apprentices. Our system now understands over 40 gesture commands that artisans use to direct robotic assistants during complex assembly processes, creating a fluid workflow that preserves creative momentum. This intuitive interaction has reduced the training time for new artisans from 6 months to 6 weeks by allowing them to focus on craft skills rather than technical interfaces.
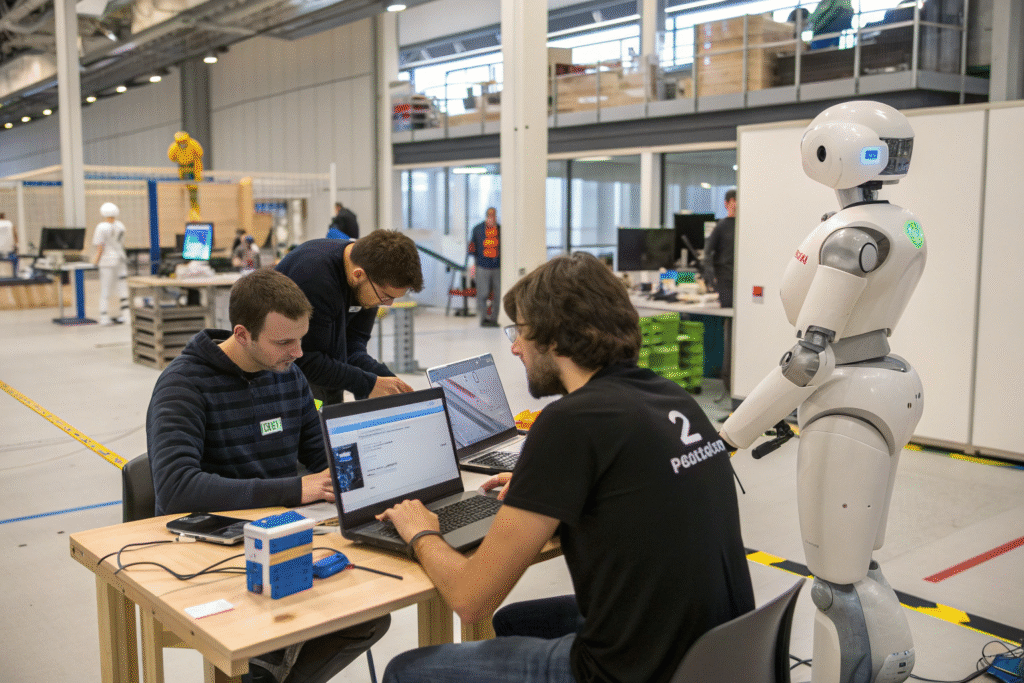

Conclusion
The future of human-robot collaboration in fashion accessories represents a fundamental reimagining of manufacturing, where the distinct capabilities of humans and machines combine to create products that neither could produce alone. This symbiotic relationship preserves the artistry and soul of handmade accessories while achieving levels of precision, consistency, and customization previously unimaginable.
As the technologies mature and become more accessible, we'll see a new era of accessory manufacturing that transcends the traditional trade-offs between scale and artistry, efficiency and uniqueness, tradition and innovation. The factories that embrace this collaborative future will define the next generation of fashion accessories, creating products that resonate deeply with consumers seeking both aesthetic beauty and personal relevance.
If you're interested in exploring human-robot collaboration for your accessory production or want to partner with a manufacturer at the forefront of this transformation, we invite you to contact our Business Director, Elaine. She can discuss our collaborative manufacturing approach and how it creates unique value for brands and consumers. Reach her at: elaine@fumaoclothing.com.










